Sasse Laboratory
The overarching research focus of the Sasse group is the development of new methods for the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Using optogenetic methods, in which light-sensitive proteins are introduced into heart cells, the group aims to develop novel tools and cellular models to expand the mechanistic understanding of cardiac arrhythmia generation and termination.
Prof. Dr. med. Philipp Sasse
Institut für Physiologie I
Nussallee 11
53115 Bonn
Research

The group showed the potential of optogenetics in the heart in vivo in 2010 and since then contributed significantly to the field of cardiac optogenetics with key publications reporting optogenetic manipulation of signaling cascades, analysis of fibroblast-cardiomyocyte coupling, gene transfer-enabled cardiac optogenetics and optogenetic defibrillation and cardioversion. Using novel optogenetic tools, the group aims to gain new insights into cardiac arrhythmia mechanisms and to develop novel therapeutic concepts as well as drug screening for pro- and anti-arrhythmic effects. For the investigation of inherited cardiac arrhythmias, the Sasse group used induced pluripotent stem cells, which can be obtained from skin biopsies and differentiated into cardiac muscle cells, and was able to show that "Long QT Syndrome 3" can be investigated in the culture dish.
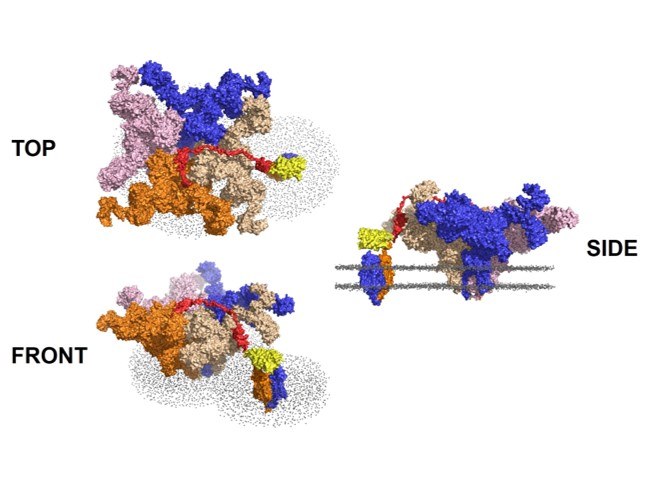
OptoRyR2
Optogenetics enable Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release from intracellular stores via the cardiac ryanodine receptor

Optogenetic Adrenergic Stimulation
Optogenetic stimulation of Gs signaling increases ventricular arrhythmia triggering from the endocardium and modulates arrhythmia maintenance and complexity
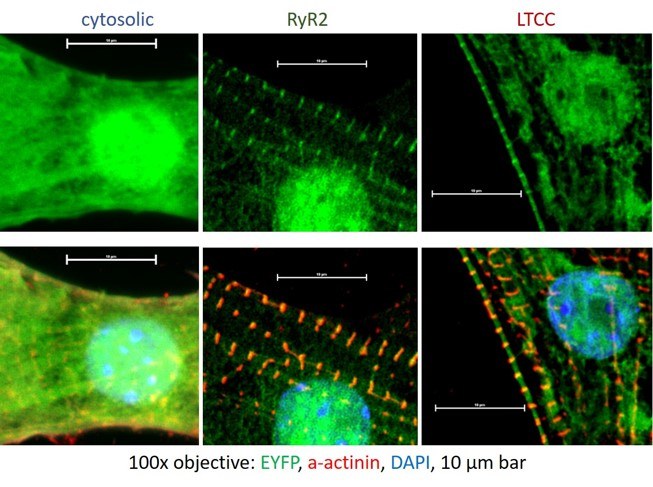
Targeted Optogenetics
Subcellular control of cAMP microdomain signaling in cardiomyocytes using targeted optogenetics
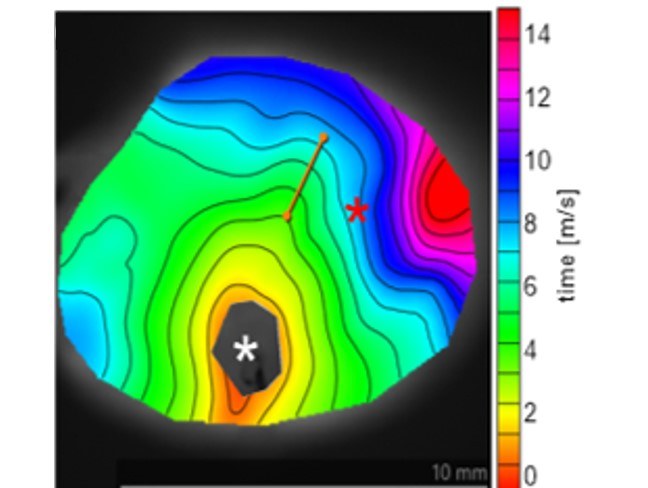
Optogenetics and Optical Voltage Mapping
Investigation of the impact of resting membrane potential and extracellular K+ concentration on cardiac conduction using optogenetics and optical voltage mapping
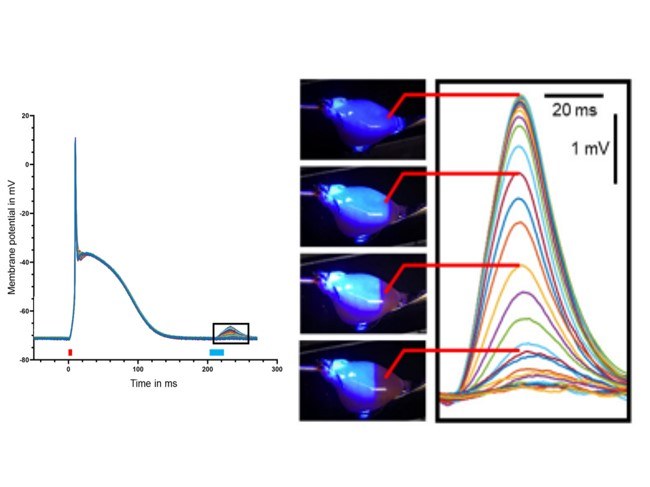
Optogenetic quantification of cardiac excitability
Optogenetic quantification of cardiac excitability and electrical coupling in intact hearts to explain cardiac arrhythmia initiation and maintenance
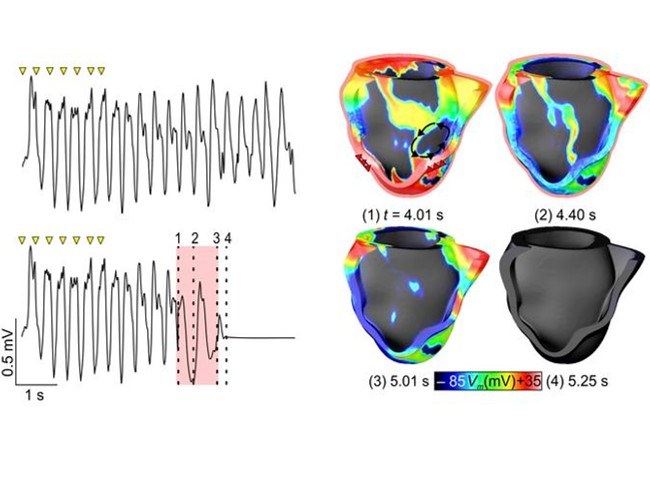
Optogenetic Pacing and Defibrillation
Wavelength-dependent light transmission in the heart wall, optogentic determination of transmural coupling and their consequences for optogenetic pacing and defibrillation
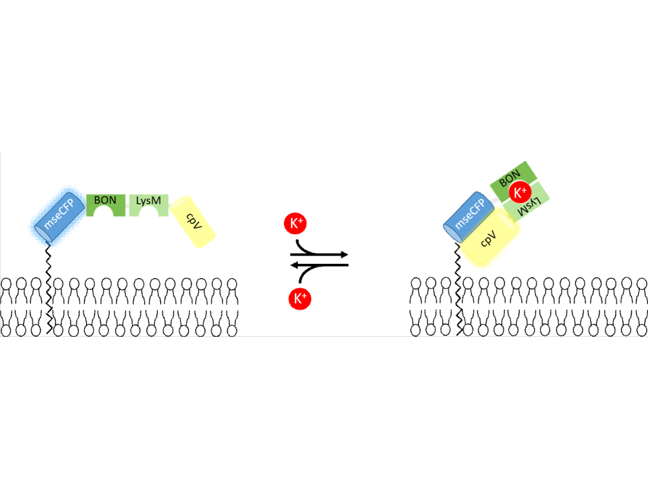
Extracellular Potassium Ion Indicator
Development of a genetically encoded extracellular potassium ion indicator

Red-shifted Optogenetics
Enzymatic vitamin A2 production enables red-shifted optogenetics

Optogenetic G-protein-coupled Receptors
Lab members
Contact
Institut für Physiologie I
Nussallee 11
53115 Bonn

Research assistants / postdocs
Wanchana Jangsangthong Dr. nat. med.
Technical assistants
Doctoral students
Alumni
Dr. rer. nat. Berivan Mansuroglu
Dr. med. Johanna Gerhards
Dr. med. Jakob Pantenburg
Milan Cokic
Dr. med. Susanne Rehnelt
Dr. med. Maximilian Funken
Dr. med. Philipp Makowka
Dr. med. Hendrik Lapp
Dr. rer. nat. Christopher Vogt
Prof. Dr rer. nat. Dr. med. Tobias Brügmann
Dr. med. Thomas Beiert
Dr. med. Thorsten Becker
Top-Publications
Optogenetic quantification of cardiac excitability and electrical coupling in intact hearts to explain cardiac arrhythmia initiation
Authors: Judith S. Langen, Patrick M. Boyle, Daniela Malan, Philipp Sasse
Sci. Adv. 2025, 11. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adt4103
Optogenetic stimulation of Gs-signaling in the heart with spatio-temporal precision
Authors: Philipp Makowka, Tobias Bruegmann, Vanessa Dusend, Daniela Malan, Thomas Beiert, Michael Hesse, Bernd K. Fleischmann, Philipp Sasse
Nat. Commun. 2019, 10:1281. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09322-7
Optogenetic termination of atrial fibrillation in mice
Authors: Bruegmann T, Beiert T, Vogt CC, Schrickel JW, Sasse P.
Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114:713-723. DOI:10.1093/cvr/cvx250
Optogenetic defibrillation terminates ventricular arrhythmia in mouse hearts and human simulations
Authors: Bruegmann T, Boyle PM, Vogt CC, Karathanos TV, Arevalo HJ, Fleischmann BK, Trayanova NA, Sasse P.
J. Clin. Invest.2016, 126:3894–3904. DOI: 10.1172/JCI88950
Human iPS Cell Model of Type 3 Long QT Syndrome Recapitulates Drug-Based Phenotype Correction
Authors: Malan D, Zhang M, Stallmeyer B, Müller J, Fleischmann BK, Schulze-Bahr E, Sasse P*, Greber B*. (*:korrespondierende Autoren)
Basic Res. Cardiol. 2016, 111:14. DOI: 10.1007/s00395-016-0530-0
More Publications
Job advertisements
Exciting topics for your bachelor or master thesis
Are you looking for an application-oriented and practice-relevant topic from the field of biomedical sciences for your thesis? Would you like to conduct optogenetic research?
We are offering an exciting opportunity and a position for your bachelor’s or master’s thesis, as well as close supervision. For details, please contact
Dr. Wanchana Jangsangthong
Mail: wjan@uni-bonn.de
Position for Master’s thesis
Optogenetics for Cardiac Cellular Mechanism and High-Throughput Screening (HTS)

